Rear-Facing Car Seats
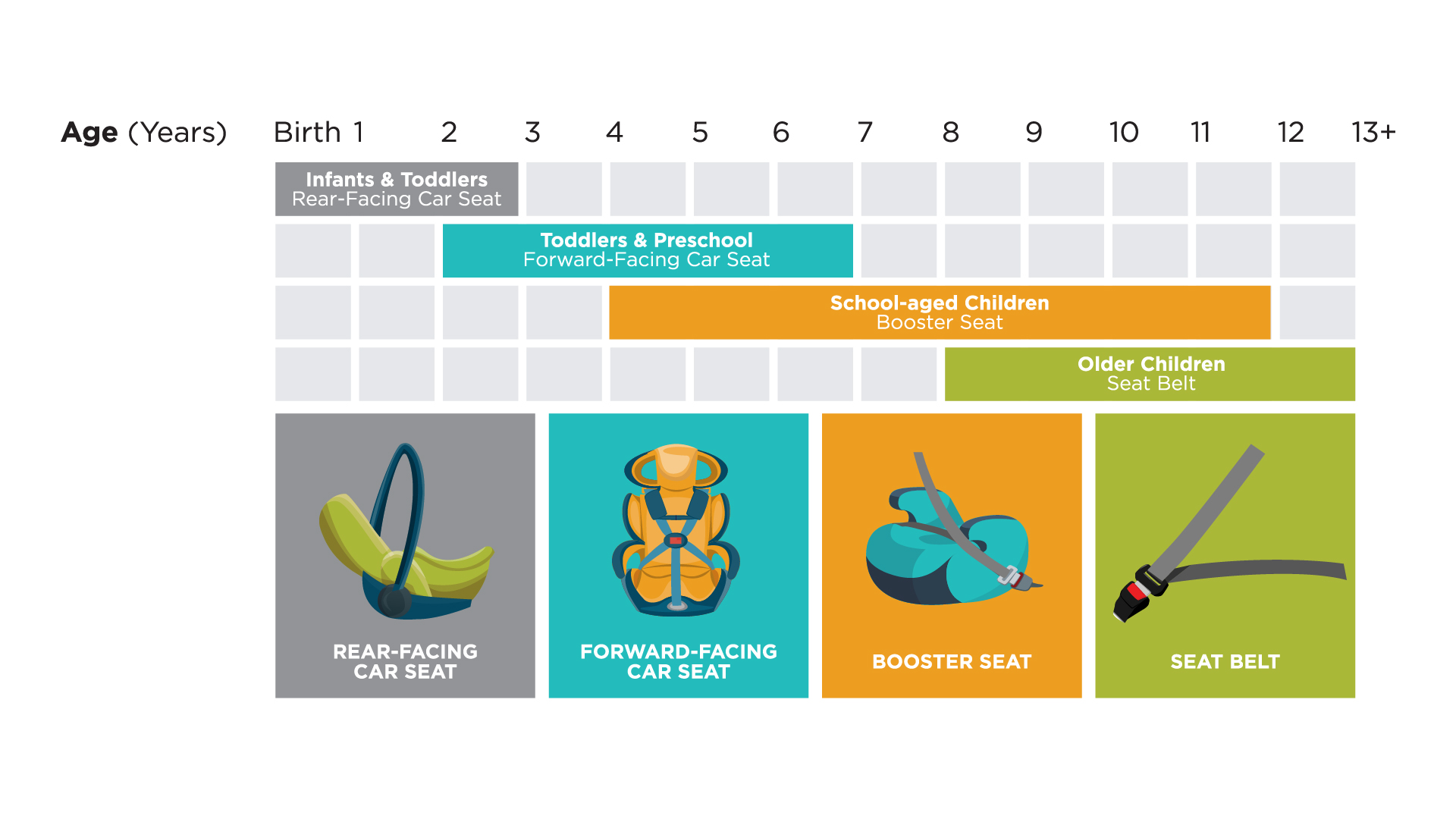
Children Should Ride Rear-Facing as Long as Possible
Remember:
- Check the labels on your car seat for height and weight limits, installation instructions, manufacturer dates and model numbers.
- The longer you keep your child rear-facing the safer they will be.
- The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that parents keep their toddler rear-facing as long as possible, until they reach the highest weight or height allowed by the car seat manufacturer.
- Most convertible seats have limits that will permit children to ride rear-facing for 2 years or longer.
- Never put your rear-facing car seat in the front passenger seat of a vehicle with airbags.
When selecting a car seat ask yourself these questions:
- Does the car seat fit your child correctly?
- Is the car seat easy for you to use?
- Does the car seat fit your car?
- Can you install the car seat correctly every time?
Remember:
- Use the car seat until your child reaches the top height or weight allowed by the manufacturer.
- Remember to check out the height and weight allowed by the manufacturer.
Car Seat Recommendations
Location and Direction of Your Car Seat in the Vehicle
Never put your rear-facing car seat in the front passenger seat of a vehicle with airbags.
The back seat is safest.
Installing a Car Seat
- Read your child’s safety seat instructions or view installation online at your manufacturer’s website. This will help you know the right way to use and install your car seat.
- Contact a certified Child Passenger Safety (CPS) technician near you.
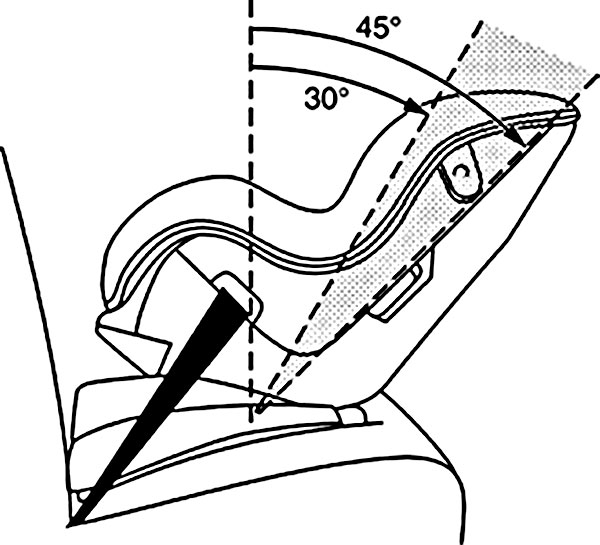
- Recline the rear-facing car seat to a 30- to 45- degree angle to avoid stress to your infant’s neck and back and to keep his head from falling forward. If an infant’s head falls forward, it could prevent him from breathing.
- Convertible car seats have two seat belt paths (rear-facing and forward-facing).
- Make sure you choose the correct belt path. Reference your car seat instructions.
- Choose either a seat belt or lower anchors. Never use both at the same time.
- Install the car seat tightly.
- Once installed, the seat should not move at the belt path more than 1 inch from side to side or back to front.
- Lower Anchors and Tethers for Children (LATCH) is a system used to install car seats in a vehicle. Refer to your vehicle owner’s manual to see if LATCH is available in your car.
- If choosing LATCH, check your vehicle owner’s manual for the seating positions in your car that can use the LATCH system.
- In LATCH use, both the car seat and the vehicle must have LATCH parts that work together.
Securing Your Child
- Adjust the harness straps.
- Rear-facing: at or below your child’s shoulder level.
- Forward-facing: at or above your child’s shoulder level.
- When buckling your child, keep the chest clip at armpit level.
- The harness straps should be tight enough that you cannot pinch the webbing together vertically.
- The harness should always be touching the child.
- Avoid bulky clothing and wrapping your child in a blanket before harnessing your child. Cover your child with a blanket or a bulky coat last, if needed.

Español
Rear-Facing Car Seats
New Parents
- All hospitals require parents to provide a car seat for their baby before leaving the hospital. However, few doctors or nurses are Certified Child Passenger Safety Technicians. Ask your care provider if there is a Child Passenger Safety Technician in the hospital that can assist you.
- Well before your baby is born, contact a nationally certified Child Passenger Safety Technician for assistance in selecting, installing and properly using your car seat.


Special Considerations
- For information on infants that need to be transported lying down, visit the “Special Needs” section on this website.
- You may place rolled cloth diapers or a thin blanket on both sides of your infant’s body (never place rolled blankets or clothes above mid-ear) and between his legs to prevent slouching or sliding. Never put rolled blankets around the top of your infant’s head. The towel could slip behind your child’s head causing the head to move forward, cutting off the infant’s airway.
- Car seats are not designed to be used with children in bulky clothing. The more compressible the outerwear is, the looser the harness becomes and the greater the risk that is posed to your child in a crash.
- Do not put padding behind your child’s back or under his bottom. If an insert did not come with the car seat, do not use one.
- Non-approved products are items that did not originally come with the car seat. These items may be harmful to your child. This also includes mirrors, toys, car seat inserts, etc. Check with your car seat manufacturer to see what they allow.
- Never leave your child alone in a vehicle.
Rear-Facing FAQs
Some car seat manufacturers recommend that you tether rear-facing. Check your car seat instructions.
It is not recommended to use a car seat as a place for your infant to sleep. A recent study in the Journal of Pediatrics found that the car seat’s harness can compress the chest wall and reduce airway size, which could result in lower oxygen levels in the blood. For more information and special considerations, contact your child’s doctor.
The handle position varies from car seat to car seat. It is important to check the car seat instructions.
Both are safe when used correctly. Never use the seat belt and lower anchors together. Select the method that secures your car seat best. Use the top tether whenever it is possible and when allowed by the car seat manufacturer and the vehicle manufacturer.
Children’s legs when seated in a rear-facing car seat may touch the back of the vehicle seat. This does not present a safety concern and children quickly adapt to the situation and learn to position their legs in a comfortable position. The fact remains that children up to age two and even older are better protected in a rear-facing car seat.
Car seats and booster seats in a vehicle always have to be replaced after a moderate or severe crash. Always check with the car seat manufacturer for recommendations if the crash was minor. NHSTA recommends the following criteria for assessing a child restraint in a minor crash:
- No visible cracks or deformities can be seen by inspecting the car seat or booster seat
- The vehicle involved in the crash can be driven from the scene
- The vehicle door nearest the car seat is undamaged
- There were no occupant injuries
- Airbags didn’t deploy
After a crash, talk to your vehicle insurance company to discuss options for a car seat and/or booster replacement.
Seat belts in cars made before 1996 may need a locking clip. Always read the instruction manuals for your vehicle and your car seat. If your car seat needs a locking clip, place it on the lap and shoulder belts, one-half to one inch from the seat belt buckle.
All car seats should meet Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards 213. Check for this on the label before you buy a car seat.
Harness straps must be at or below the rear-facing child’s shoulders.
Locate the belt path arrow or label on your car seat for the correct belt path use. Follow the car seat manufacturer’s instructions.
Yes! All car seat owners are strongly encouraged to register the car seat with the manufacturer either online or by mailing in the registration card. Manufacturers need your information to contact you about safety issues, including recalls, and are not allowed to use owner data for other purposes.
A convertible car seat can be used as a rear-facing car seat and once the toddler has reached the weight or height limit, the car seat can be changed to the forward-facing position. See your car seat directions for more information about weight/height limits and how to change from a rear-facing car seat to a forward-facing car seat.
It is recommended that children ride in an appropriate car seat or booster seat in the back seat until the age of 13 years. In Utah, this recommendation isn’t part of the law and drivers cannot be cited if a child younger than age 13 is found riding in the front seat. However, the back seat is generally the safest place in the vehicle and it is considered “best practice” to secure young children in rear seating positions. If a back seat is not available, parents can secure children in front seating positions and should make sure the child is using an appropriate restraint and that the car seat or booster seat is used according to manufacturer’s instructions. Also, parents should move the vehicle seat as far back as possible. Please note that if a passenger side airbag is present, rear-facing infants should not be placed in the front seat unless the airbag is turned off.